Understanding Female and Male Cannabis Plants: Identification and Best Practices
- Jun 20, 2024
- 3 min read
Cannabis cultivation requires a fundamental understanding of the plant's biology, particularly the differences between male and female plants. This knowledge is crucial for growers, especially those focused on producing high-quality buds. In this blog post, we'll explore the differences between female and male cannabis plants, the best point in the growth cycle to determine their sex, and offer best practices for identifying their gender.
The Basics: Female vs. Male Cannabis Plants
Female Cannabis Plants
Female cannabis plants are highly valued in both medicinal and recreational cannabis cultivation. They produce the resinous buds that contain high levels of cannabinoids such as THC and CBD, which are essential for the plant's desired effects.
Characteristics:
Buds: Female plants develop flowers or "buds" covered in trichomes, which are rich in cannabinoids.
Pistils: These are hair-like structures, usually white to orange, emerging from the calyxes. They help catch pollen from male plants.
Calyxes: Small, teardrop-shaped nodes where pistils emerge, forming the dense buds.
Male Cannabis Plants
Male cannabis plants are primarily used for breeding purposes. They produce pollen, which is necessary for fertilizing female plants and producing seeds. However, for growers focused on bud production, male plants are usually undesirable.
Characteristics:
Pollen Sacs: Male plants develop small, round sacs at the nodes, which release pollen.
Lack of Buds: Unlike female plants, male plants do not produce significant buds with cannabinoids.
Best Point in the Growth Cycle to Determine Sex
Identifying the sex of cannabis plants early in the growing cycle is crucial. The best time to do this is during the pre-flowering stage, which usually occurs between the 4th and 6th weeks of growth, depending on the strain and growing conditions.
1. Vegetative Stage (Weeks 1-3)
Growth Focus: During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants focus on growing leaves, stems, and roots. At this stage, the plants are not yet showing signs of their sex.
Observation: You won’t be able to determine the sex of your plants during the early vegetative stage. Instead, focus on ensuring they receive proper light, nutrients, and water to promote healthy growth.
2. Pre-Flowering Stage (Weeks 4-6)
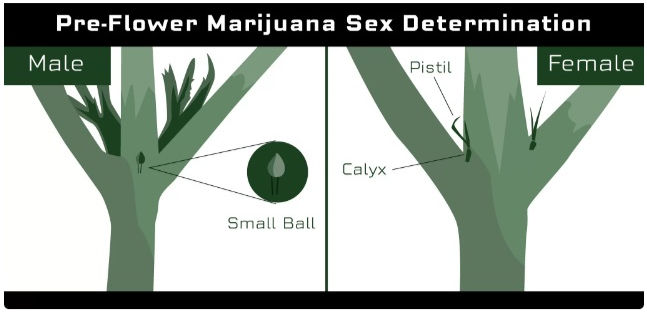
Onset of Pre-Flowering: As cannabis plants transition from the vegetative stage to the flowering stage, they enter the pre-flowering stage. This is when the first signs of sex will become visible.
Identifying Females: Female plants start to show their sex by developing small, hair-like structures called pistils at the nodes (where the branches meet the main stem). These white, wispy hairs indicate the presence of female reproductive organs.
Identifying Males: Male plants will develop small, round balls or pollen sacs at the nodes. These sacs will eventually open to release pollen, but at this stage, they are still closed and can be identified before they pollinate female plants.
3. Early Flowering Stage (Weeks 7-8)
Further Development: If you haven’t identified and separated the males during the pre-flowering stage, you can still do so in the early flowering stage. By now, the characteristics of each sex will be more pronounced.
Immediate Action: It’s crucial to remove male plants as soon as you identify them to prevent them from pollinating the females, which would result in seed production rather than bud development.
Best Practices for Identifying and Managing Sex
Regular Monitoring: Check your plants daily during the pre-flowering stage to catch the first signs of their sex.
Separate Early: As soon as you identify a male plant, remove it from the growing area to protect your female plants.
Use Clones: To avoid the hassle of sexing plants, start with clones from a known female plant. This ensures that all your plants are female and will produce buds.
Why Identifying Male Plants Early Is Important
Male plants can pollinate female plants, leading to seed production rather than bud development. This can significantly impact the quality and yield of your harvest. By identifying and removing male plants early, you can ensure that your female plants produce the maximum amount of potent, seedless buds (known as sensimilla).
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between female and male cannabis plants and implementing best practices for early identification is key to successful cannabis cultivation. The pre-flowering stage, between weeks 4 and 6, is the optimal time to determine the sex of your cannabis plants. By closely monitoring your plants during this period, you can identify and remove male plants before they can pollinate the females, ensuring a high-quality, seedless harvest.
Happy growing!





Comments